Plots
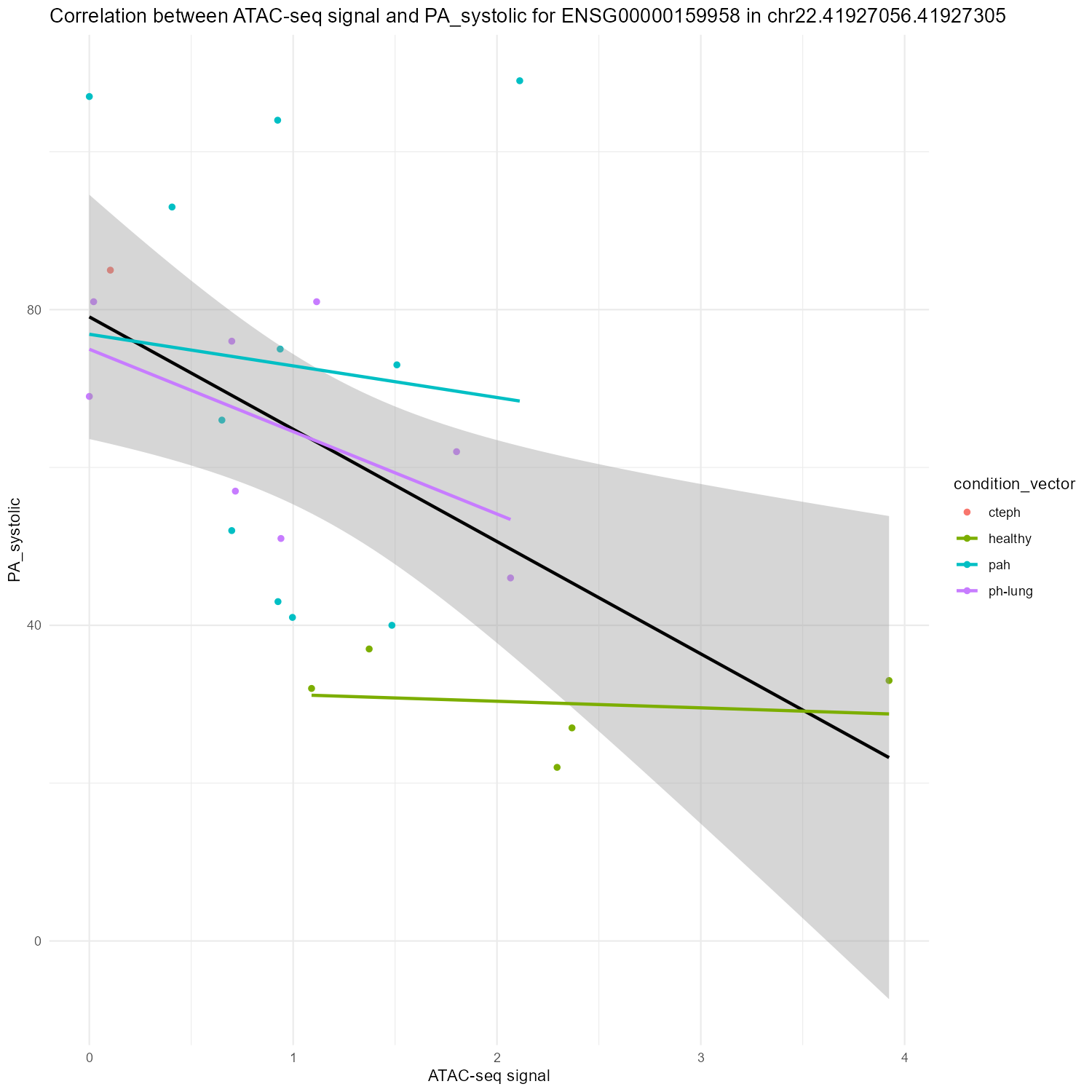
PA_sys
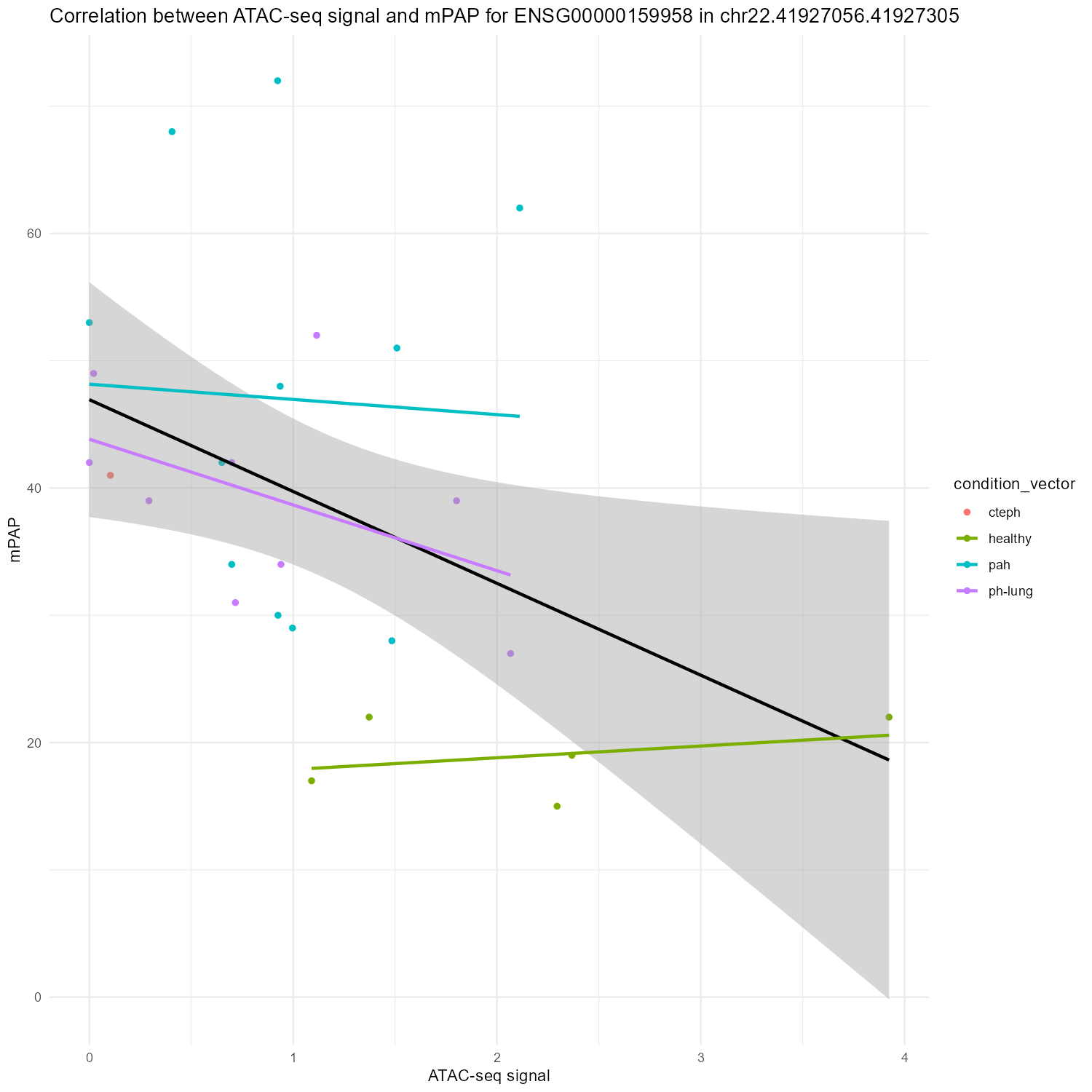
mPAP
Info
TNFRSF13B c.226G>A (p.Gly76Ser) as a Novel Causative Mutation for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Shinya, Y., Hiraide, T., Momoi, M., Goto, S., Suzuki, H., Katsumata, Y., Kurebayashi, Y., Endo, J., Sano, M., Fukuda, K., Kosaki, K., & Kataoka, M. (2021). TNFRSF13B c.226G>A (p.Gly76Ser) as a Novel Causative Mutation for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of the American Heart Association: Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease, 10. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.120.019245.
NCBI Gene Summary for TNFRSF13C Gene
- B cell-activating factor (BAFF) enhances B-cell survival in vitro and is a regulator of the peripheral B-cell population. Overexpression of Baff in mice results in mature B-cell hyperplasia and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Also, some SLE patients have increased levels of BAFF in serum. Therefore, it has been proposed that abnormally high levels of BAFF may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by enhancing the survival of autoreactive B cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for BAFF and is a type III transmembrane protein containing a single extracellular cysteine-rich domain. It is thought that this receptor is the principal receptor required for BAFF-mediated mature B-cell survival. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
GeneCards Summary for TNFRSF13C Gene
TNFRSF13C (TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 13C) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with TNFRSF13C include Immunodeficiency, Common Variable, 4 and Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Among its related pathways are Akt Signaling and TGF-Beta Pathway. An important paralog of this gene is TNFRSF17.